简介
指令带有前缀 v-,以表示它们是 Vue 提供的特殊特性。
v-bind, v-if, v-for, v-on
绑定数据
1
2
3
4
5
| <div id="app">
<span v-bind:title="message">
鼠标悬停几秒钟查看此处动态绑定的提示信息!
</span>
</div>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| var app2 = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: '页面加载于 ' + new Date().toLocaleString()
}
})
|
表单输入绑定
你可以用 v-model 指令在表单 <input> 及 <textarea> 元素上创建双向数据绑定。
默认的 prop 为 value, event 为 input。
1
2
| <input v-model="message" placeholder="edit me">
<p>Message is: </p>
|
src/core/vdom/create-component.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| function transformModel (options, data: any) {
const prop = (options.model && options.model.prop) || 'value'
const event = (options.model && options.model.event) || 'input'
;(data.attrs || (data.attrs = {}))[prop] = data.model.value
const on = data.on || (data.on = {})
const existing = on[event]
const callback = data.model.callback
if (isDef(existing)) {
if (
Array.isArray(existing)
? existing.indexOf(callback) === -1
: existing !== callback
) {
on[event] = [callback].concat(existing)
}
} else {
on[event] = callback
}
}
|
参数
一些指令能够接收一个“参数”,在指令名称之后以冒号表示。例如,v-bind 指令可以用于响应式地更新 HTML 特性:
1
| <a v-bind:href="url">...</a>
|
在这里 href 是参数,告知 v-bind 指令将该元素的 href 特性与表达式 url 的值绑定。
另一个例子是 v-on 指令,它用于监听 DOM 事件:
1
| <a v-on:click="doSomething">...</a>
|
在这里参数是监听的事件名。我们也会更详细地讨论事件处理。
缩写
Vue.js 为 v-bind 和 v-on 这两个最常用的指令,提供了特定简写:
v-bind
1
2
3
4
5
| <!-- 完整语法 -->
<a v-bind:href="url">...</a>
<!-- 缩写 -->
<a :href="url">...</a>
|
v-on
1
2
3
4
5
| <!-- 完整语法 -->
<a v-on:click="doSomething">...</a>
<!-- 缩写 -->
<a @click="doSomething">...</a>
|
单文件组件
文件扩展名为 .vue 的 single-file components(单文件组件)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <template>
<!-- ...模板 -->
</template>
<script>
// ...
</script>
<style>
/* ... */
</style>
|
自定义组件
Props
Type Checks
In addition, type can also be a custom constructor function and the assertion will be made with an instanceof check. For example, given the following constructor function exists:
1
2
3
4
| function Person (firstName, lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName
this.lastName = lastName
}
|
You could use:
1
2
3
4
5
| Vue.component('blog-post', {
props: {
author: Person
}
})
|
to validate that the value of the author prop was created with new Person.
Non-Prop Attributes
Reactivity in Depth
Due to the limitations of modern JavaScript (and the abandonment of Object.observe), Vue cannot detect property addition or deletion. Since Vue performs the getter/setter conversion process during instance initialization, a property must be present in the data object in order for Vue to convert it and make it reactive.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| var vm = new Vue({
data: {
a: 1
}
})
// `vm.a` is now reactive
vm.b = 2
// `vm.b` is NOT reactive
|
When you pass a plain JavaScript object to a Vue instance as its data option, Vue will walk through all of its properties and convert them to getter/setters using Object.defineProperty.
Every component instance has a corresponding watcher instance, which records any properties “touched” during the component’s render as dependencies. Later on when a dependency’s setter is triggered, it notifies the watcher, which in turn causes the component to re-render.
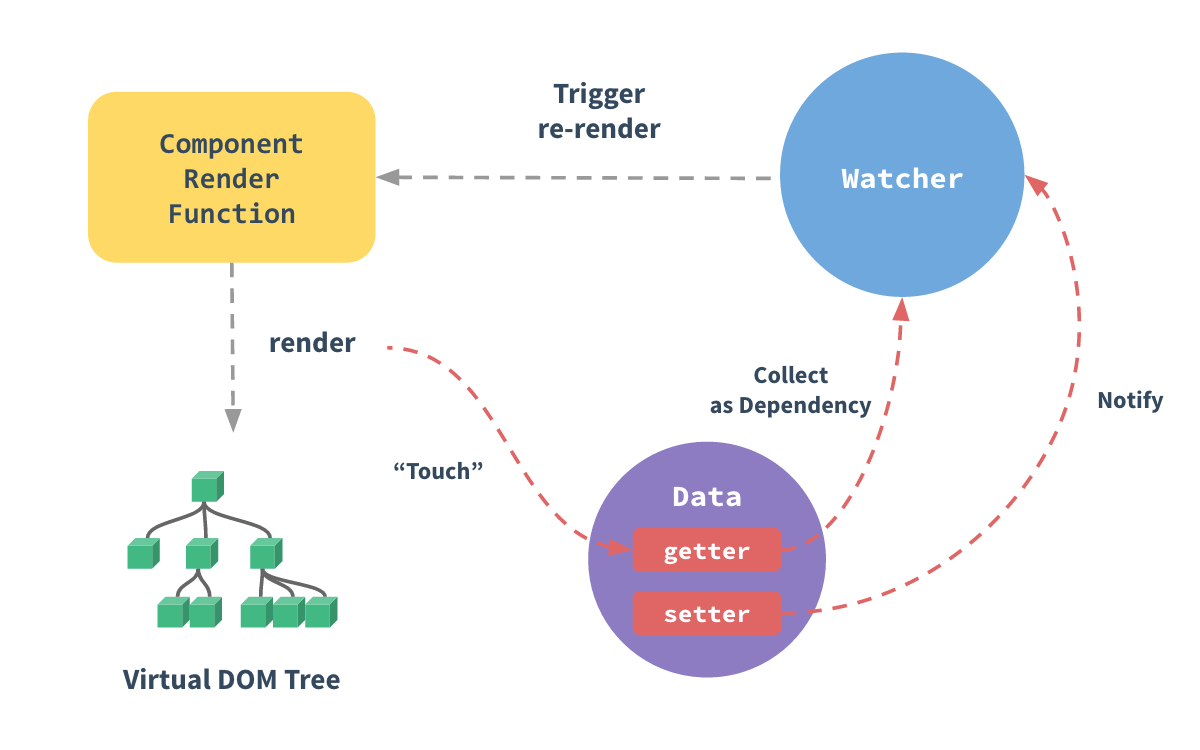
Vue does not allow dynamically adding new root-level reactive properties to an already created instance. However, it’s possible to add reactive properties to a nested object using the Vue.set(object, propertyName, value) method:
1
| Vue.set(vm.someObject, 'b', 2)
|
You can also use the vm.$set instance method, which is an alias to the global Vue.set:
1
| this.$set(this.someObject, 'b', 2)
|
For Arrays
Vue cannot detect the following changes to an array:
- When you directly set an item with the index, e.g.
vm.items[indexOfItem] = newValue
1
2
| Vue.set(vm.items, indexOfItem, newValue)
Vue.delete( target, propertyName/index )
|
Vue performs DOM updates asynchronously.
you can use Vue.nextTick(callback) immediately after the data is changed.
Event Handling
Event Modifiers
1
2
3
4
5
| <!-- the click event's propagation will be stopped -->
<a v-on:click.stop="doThis"></a>
<!-- the submit event will no longer reload the page -->
<form v-on:submit.prevent="onSubmit"></form>
|
Transitions
1
2
3
| <transition name="fade">
<p v-if="show">hello</p>
</transition>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| .fade-enter-active, .fade-leave-active {
transition: opacity .5s;
}
.fade-enter, .fade-leave-to /* .fade-leave-active below version 2.1.8 */ {
opacity: 0;
}
|
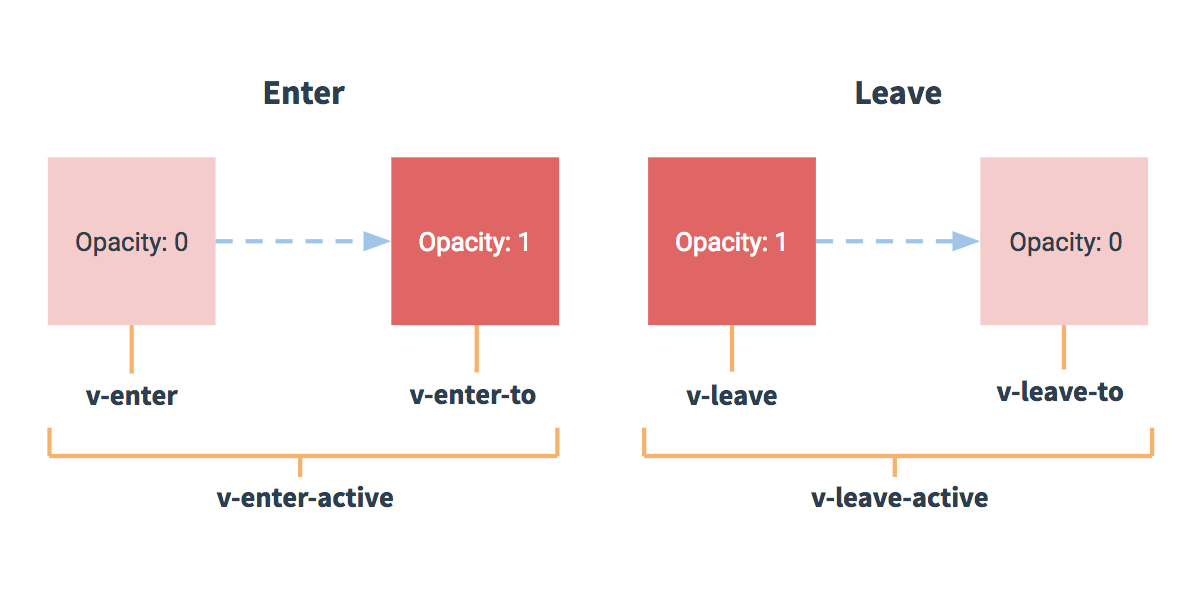
Transition Classes
v-enterv-enter-activev-enter-tov-leavev-leave-activev-leave-to
插件
通过全局方法 Vue.use() 使用插件。它需要在你调用 new Vue() 启动应用之前完成:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| // 调用 `MyPlugin.install(Vue)`
Vue.use(MyPlugin)
new Vue({
// ...组件选项
})
|
Directive
1
2
3
4
5
| bind()
inserted()
update()
componentUpdated()
unbind()
|
Params:
1
| (el, binding, vnode, oldVnode)
|
VNode
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| {
tag: string | void;
data: VNodeData | void;
children: ?Array<VNode>;
text: string | void;
elm: Node | void; // 当前 VNode 对应的真实dom节点
ns: string | void;
context: Component | void; // rendered in this component's scope
key: string | number | void;
componentOptions: VNodeComponentOptions | void;
componentInstance: Component | void; // component instance
parent: VNode | void; // component placeholder node
// ......
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| declare interface VNodeData {
key?: string | number;
slot?: string;
ref?: string;
is?: string;
pre?: boolean;
tag?: string;
staticClass?: string;
class?: any;
staticStyle?: { [key: string]: any };
style?: string | Array<Object> | Object;
normalizedStyle?: Object;
props?: { [key: string]: any };
attrs?: { [key: string]: string };
domProps?: { [key: string]: any };
hook?: { [key: string]: Function };
on?: ?{ [key: string]: Function | Array<Function> };
nativeOn?: { [key: string]: Function | Array<Function> };
transition?: Object;
show?: boolean; // marker for v-show
inlineTemplate?: {
render: Function;
staticRenderFns: Array<Function>;
};
directives?: Array<VNodeDirective>;
keepAlive?: boolean;
scopedSlots?: { [key: string]: Function };
model?: {
value: any;
callback: Function;
};
};
|
Vue
全局 API
Vue.extend
选项 / DOM
el
template
render
Vue 选项中的 render 函数若存在,则 Vue 构造函数不会使用 template 选项或 el 选项编译渲染。
实例方法
vm.$mount
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| var MyComponent = Vue.extend({
template: '<div>Hello!</div>'
})
// 在文档之外渲染并且随后挂载
var component = new MyComponent().$mount()
document.getElementById('app').appendChild(component.$el)
|
生命周期(Lifecycle)
- beforeCreate
- created
- beforeMount
- mounted
- beforeUpdate
- updated
- activated
- deactivated
- beforeUnmount
- unmounted
- errorCaptured
- renderTracked
- renderTriggered
Vue Router
Navigation Guards
https://router.vuejs.org/
Tricks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| // nest
new Router({
routes: [{
path: '/parent',
component: {
render: (h) => h('router-view'),
},
children: [
{
path: '' /** default */,
component: ...
},
{
path: 'create',
component: ...
},
]
}]
})
|
Vuex
State
mapState 辅助函数
当映射的计算属性的名称与 state 的子节点名称相同时,我们也可以给 mapState 传一个字符串数组。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| export default {
computed: {
...mapState([
// 映射 this.count 为 store.state.count
'count'
])
}
}
|
Getter
可以认为是 store 的计算属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| const store = new Vuex.Store({
// ...
getters: {
doneTodos: state => {
return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done)
}
// getter 作为第二个参数,可以调用其他 getter
doneTodosCount: (state, getters) => {
return getters.doneTodos.length
}
}
})
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| export const store = new Vuex.Store({
// ...
// 带参数的Getter
getters: {
getSubToc: state => (...path) => _.get(state.toc, path),
}
})
|
mapGetters 辅助函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters([
'doneTodosCount',
'anotherGetter',
// ...
])
}
}
|
Mutation
Mutation 需遵守 Vue 的响应规则
既然 Vuex 的 store 中的状态是响应式的,那么当我们变更状态时,监视状态的 Vue 组件也会自动更新。这也意味着 Vuex 中的 mutation 也需要与使用 Vue 一样遵守一些注意事项:
最好提前在你的 store 中初始化好所有所需属性。
当需要在对象上添加新属性时,你应该
使用 Vue.set(obj, 'newProp', 123), 或者
以新对象替换老对象。例如,利用 stage-3 的对象展开运算符我们可以这样写:
1
| state.obj = { ...state.obj, newProp: 123 }
|
mutation 必须是同步函数。在 Vuex 中,mutation 都是同步事务:
1
2
| store.commit('increment')
// 任何由 "increment" 导致的状态变更都应该在此刻完成。
|
使用常量替代 Mutation 事件类型
把这些常量放在单独的文件中可以让你的代码合作者对整个 app 包含的 mutation 一目了然
Action
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
Action 通过 store.dispatch 方法触发:
1
| store.dispatch('increment')
|
https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/
Class Component
https://class-component.vuejs.org/
install
1
| npm install --save vue vue-class-component
|
TypeScript
Babel
Data
1
2
3
| <template>
<div></div>
</template>
|
1
2
3
4
5
| @Component
export default class HelloWorld extends Vue {
// Declared as component data
message = 'Hello World!'
}
|
Methods
1
2
3
| <template>
<button v-on:click="hello">Click</button>
</template>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Component
export default class HelloWorld extends Vue {
// Declared as component method
hello() {
console.log('Hello World!')
}
}
|
Computed
Computed properties can be declared as class property getter / setter:
1
2
3
| <template>
<input v-model="name">
</template>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| @Component
export default class HelloWorld extends Vue {
firstName = 'John'
lastName = 'Doe'
// Declared as computed property getter
get name() {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName
}
// Declared as computed property setter
set name(value) {
const splitted = value.split(' ')
this.firstName = splitted[0]
this.lastName = splitted[1] || ''
}
}
|
Hooks
data, render and all Vue lifecycle hooks can be directly declared as class prototype methods.
Other Options
For all other options, pass them to the decorator function:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @Component({
components: {
OtherComponent
},
setup(rops, context) {
// ...
}
})
export default class HelloWorld extends Vue {}
|
Additional Hooks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import Component from 'vue-class-component'
// Register the router hooks with their names
Component.registerHooks([
'beforeRouteEnter',
'beforeRouteLeave',
'beforeRouteUpdate'
])
|
Custom Decorators
Property Type Declaration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| @Component({
computed: mapGetters([
'posts'
]),
methods: mapActions([
'fetchPosts'
])
})
export default class Posts extends Vue {
posts!: Post[]
fetchPosts!: () => Promise<void>
}
|
$refs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| export default class InputFocus extends Vue {
$refs!: {
input: HTMLInputElement
}
// ...
}
|
Property Decorator
https://github.com/kaorun343/vue-property-decorator
简易绑定
getter setter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| var obj = {
data: {
a: 1
},
get a() {
return this.data.a
},
set a(val) {
this.data.a = val
}
}
obj.a // 1
obj.a = 2
obj.a // 2
obj.data.a // 2
|
defineProperty
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| var obj = {
data: {
num: 10,
name: 'sword'
},
}
for(let prop in obj.data) {
Object.defineProperty(obj, prop, {
get: function(){
return obj.data[prop]
},
set: function(val){
obj.data[prop] = val
}
})
}
obj.num // 10
obj.name // "sword"
obj.name = "armour"
obj.data.name // "armour"
|
Render Functions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| Vue.component('anchored-heading', {
render: function (createElement) {
return createElement(
'h' + this.level, // tag name
this.$slots.default // array of children
)
},
props: {
level: {
type: Number,
required: true
}
}
})
|
1
2
| <anchored-heading :level="1">Hello world!</anchored-heading>
<anchored-heading :level="2">test</anchored-heading>
|
render 的返回值为 VNode
https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/render-function.html
JSX
https://github.com/vuejs/jsx
1
2
3
| render() {
return <p>hello</p>
}
|
Attributes/Props
1
2
3
| render() {
return <MyShare options={this.options} onSelect={this.onOptionSelect} />;
},
|
Slots
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| render() {
return (
<MyComponent>
<header slot="header">header</header>
<footer slot="footer">footer</footer>
</MyComponent>
)
}
|
Directives
1
| <input vModel={this.newTodoText} />
|
1
| <input vOn:click_stop_prevent={this.newTodoText} />
|
v-html:
1
| <p domPropsInnerHTML={html} />
|
Composition API
The new setup component option is executed before the component is created.
We can make any variable reactive anywhere with a new ref function.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| import { fetchUserRepositories } from '@/api/repositories'
import { ref, onMounted, watch, toRefs } from 'vue'
// in our component
setup (props) {
// using `toRefs` to create a Reactive Reference to the `user` property of props
const { user } = toRefs(props)
const repositories = ref([])
const getUserRepositories = async () => {
// update `props.user` to `user.value` to access the Reference value
repositories.value = await fetchUserRepositories(user.value)
}
onMounted(getUserRepositories)
// set a watcher on the Reactive Reference to user prop
watch(user, getUserRepositories)
return {
repositories,
getUserRepositories
}
}
|
Reactivity APIs
reactive, ref, computed, watchEffect, watch
Lifecycle Hooks
- beforeCreate -> use
setup()
- created -> use
setup()
- beforeMount -> onBeforeMount
- mounted -> onMounted
- beforeUpdate -> onBeforeUpdate
- updated -> onUpdated
- beforeDestroy ->
onBeforeUnmount
- destroyed ->
onUnmounted
- activated -> onActivated
- deactivated -> onDeactivated
Template Refs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| <template>
<div ref="root"></div>
</template>
<script>
// ...
setup() {
const root = ref(null)
onMounted(() => {
// the DOM element will be assigned to the ref after initial render
console.log(root.value) // <div/>
})
return {
root
}
}
</script>
|
Tricks
Reset Data
1
| Object.assign(this.$data, this.$options.data.apply(this))
|
chain v-model
1
| <input v-model="searchText">
|
does the same thing as:
1
2
3
4
| <input
v-bind:value="searchText"
v-on:input="searchText = $event.target.value"
>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| // Address.vue
<template>
<div>
<quill-editor v-model="content" :options="option">
<div id="toolbar" slot="toolbar" ref="toolbar">
<button class="ql-bold">Bold</button>
<button class="ql-italic">Italic</button>
<button class="ql-image"></button>
</div>
</quill-editor>
</div>
</template>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import { quillEditor } from 'vue-quill-editor';
export default {
props: ['value'],
components: { quillEditor },
computed: {
content: {
get() { return this.value; },
set(content) { this.$emit('input', content); },
},
}
}
|
router default
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| children: [
{
path: '/main',
component: Main
},
// ... other children
{
path: '', // empty path
redirect: '/main'
}
];
|
Debug
print store in console:
1
| document.getElementsByTagName('div')[0].__vue__.$store.state
|
search Vue.js v2
Set a breakpoint on this line and reload the page.
vue.esm.js
step over next function call
1
| t.exports.default.config.devtools =true;
|
Search 2.6.1 in chunk-vue.[hash].js
1
| Cr.config.devtools = true;
|
Or search .config.devtools
Vetur
Project Setup
At project root create a jsconfig.json.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| {
"include": [
"./src/**/*"
],
"compilerOptions": {
"baseUrl": ".",
"paths": {
"@/*": [
"./src/*"
]
},
}
}
|
https://vuejs.github.io/vetur/setup.html#project-setup
Nginx 部署
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| server {
listen 8066;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /path/to/app/dist;
index index.html index.htm;
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
location ~ ^/api/(.*)$ {
proxy_pass https://api.example.com;
}
}
|
Multiple Vue app:
1
2
3
4
5
| export default new Router({
mode: 'history',
base: '/app2',
routes: [...]
})
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| server {
listen 8080;
server_name localhost;
location ~ ^/app1/web {
alias /path/to/vue/app1/dist;
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html =404;
}
location ~ ^/app1/api/(.*)$ {
rewrite /app1/api/(.*)$ /$1 break;
proxy_pass http://localhost:8877;
}
location ~ ^/app2/web {
alias /path/to/vue/app2/dist;
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html =404;
}
location ~ ^/app2/api/(.*)$ {
rewrite /app2/api/(.*)$ /$1 break;
proxy_pass http://localhost:8888;
}
}
|
资料
官方指南
vue test utils

