简介
Spring MVC 基于 Servlet API 和 Spring Framework。
HelloWorld
使用Maven
首先我们新建一个目录,在里面新建一个 pom.xml
复制以下内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>gs-serving-web-content</artifactId>
<version>0.1.0</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.10.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
接下来打开Eclipse -> File -> Import… -> Existing Maven Projects -> Next
选择我们的项目 -> Finish
稍等片刻就导入成功了。
接下来新建代码目录和模板目录:
1
2
mkdir -p src/main/java/hello
mkdir -p src/main/resources/templates/
此时的目录结构如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
.
├── pom.xml
├── src
│ └── main
│ ├── java
│ │ └── hello
│ └── resources
│ └── templates
└── target
└── ...
接着创建一个Controller
src/main/java/hello/GreetingController.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
@Controller
public class GreetingController {
@RequestMapping("/greeting")
public String greeting(@RequestParam(value="name", required=false, defaultValue="World") String name, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name", name);
return "greeting";
}
}
然后创建一个模板
src/main/resources/templates/greeting.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Getting Started: Serving Web Content</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="'Hello, ' + ${name} + '!'" />
</body>
</html>
接着还要创建一个入口类
src/main/java/hello/Application.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
最后启动项目
1
mvn spring-boot:run
访问 localhost:8080/greeting 就可以看见 HelloWorld 了。
简易分析
我们简单的看一下代码
pom.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>
这里 thymeleaf 是一个模板引擎
接着看 greeting.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
...
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="'Hello, ' + ${name} + '!'" />
</body>
</html>
这里的th:text就是一个thymeleaf模板引擎的应用。
我们再看下GreetingController
src/main/java/hello/GreetingController.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
@Controller
public class GreetingController {
@RequestMapping("/greeting")
public String greeting(@RequestParam(value="name", required=false, defaultValue="World") String name, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name", name);
return "greeting";
}
}
这段代码就充满了魔法,只是一个普通的JAVA类,既没有继承抽象类也没有实现特定的接口。仅仅是加了 @Controller 这个注解。
再看greeting这个方法,只是个普通的方法。加上了 @RequestMapping("/greeting") 就表示 /greeting 这个请求是由这个方法来处理的。
参数有两个 String name, Model model
name 这个参数前面有个很长的注解 @RequestParam(value="name", required=false, defaultValue="World")
@RequestParam 把一个query String中的值传给参数。
方法的内容只有两行,第一行 model.addAttribute("name", name); 把name放进Model。
最后返回了一个字符串 greeting,这个字符串就是 View 的名字。
在SpringMVC中,Controller负责处理HTTP请求,View负责渲染HTML页面,Model则是连接Controller和View的桥梁。
小结
几个复制粘贴网站就跑起来了,非常方便。
非常的简洁,几乎没有多余的代码。
但是简洁的外表下隐藏了许多复杂的工作,想要研究它的实现原理并不容易。
所以目前只要记住格式就好了。
DispatcherServlet
Spring MVC 围绕着DispatcherServlet实现了前端控制器设计模式,DispatcherServlet 提供了公用的请求处理算法。
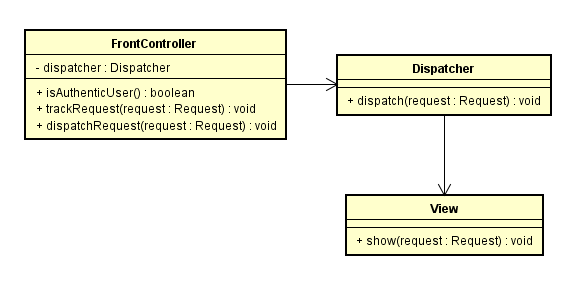
前端控制器模式
前端控制器模式(front controller pattern) 提供了一个集中的请求处理机制,所有的请求都将由同一个handler处理,这个handler可以用来认证、授权、记录日志或者跟踪请求,然后把请求交给相应的程序处理。
前端控制器模式有以下几个实体:
前端控制器(Front Controller) - 处理所有请求
调度器(Dispatcher) - 将请求调度给相应的程序
视图(View) - 处理请求
Annotated Controllers
Spring MVC 为 @Controller 和 @RestController 提供了一套基于注解的编程模型来处理请求映射,请求输入,异常处理等工作。
Annotated controllers 既不必继承与某类也不必实现特定接口,同时也可以使用灵活的函数签名。
@RequestMapping
@RequestMapping 用于将请求映射给对应的方法。@RequestMapping 可以通过许多属性来配配请求,如 URL,HTTP method,请求参数,请求头,media types 。
可以对Class添加@RequestMapping注解。
Spring MVC 也提供了一些快捷注解, 如 @GetMapping @PostMapping @PutMapping @DeleteMapping @PatchMapping
URI
我们可以使用通配符
? - 匹配一个字符
* - 匹配零个或一个字符
** - 匹配零个或多个字符
也可以定义路径变量{var},使用 @PathVariable 来获取,路径变量会转换为对应的类型。
@PathVariable 默认取和参数同名的路径变量,当然也可以指明变量名:@PathVariable("customId")。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/hotels/{hotel}")
public class BookingController {
@GetMapping("/bookings/{booking}")
public String getBooking(@PathVariable Long booking) {
// ...
}
}
{varName:regex}
1
2
3
4
@GetMapping("/{name:[a-z-]+}-{version:\\d\\.\\d\\.\\d}{ext:\\.[a-z]+}")
public void handle(@PathVariable String version, @PathVariable String ext) {
// ...
}
media types
1
2
3
4
@PostMapping(path = "/pets", consumes = "application/json")
public void addPet(@RequestBody Pet pet) {
// ...
}
Parameters
1
2
3
4
@GetMapping(path = "/pets/{petId}", params = "myParam=myValue")
public void findPet(@PathVariable String petId) {
// ...
}
Headers
1
2
3
4
@GetMapping(path = "/pets", headers = "myHeader=myValue")
public void findPet(@PathVariable String petId) {
// ...
}
参数
@RequestMapping 的方法可以选择各种各样的参数。
| 参数类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| WebRequest, NativeWebRequest | 通用参数,可以获取request参数,request属性,session属性。 |
| ServletRequest,ServletResponse | Servlet参数 |
| @RequestParam | Servlet request parameters |
| InputStream,Reader | 获取raw request body |
| OutputStream,Writer | 获取 Servlet API 提供的 raw response body |
| HttpSession | |
| Principal | 当前授权用户,可以使用实现类 |
| Locale | |
| @PathVariable | 路径参数 |
| @RequestHeader | 请求头 |
| @CookieValue | Cookie |
| @RequestBody | 请求体 |
| HttpEntity | 请求头 + 请求体 |
| Map,Model,ModelMap | 交给模板用于渲染页面 |
| @ModelAttribute | |
| Errors, BindingResult | errors from validation and data binding |
| @SessionAttribute |
……
@RequestParam
从QueryString中获取一个参数
1
2
3
public String confirmRegistration(HttpServletRequest request, Model model, @RequestParam("token") String token) {
//...
}
@RequestBody
可以把请求体映射为实体类
1
2
3
4
@PostMapping("password")
public RestResult setPayPassword(@Valid @RequestBody SetPasswordRequest request) {
//...
}
@RequestHeader
1
2
3
4
5
6
@GetMapping("/demo")
public void handle(
@RequestHeader("Accept-Encoding") String encoding,
@RequestHeader("Keep-Alive") long keepAlive) {
//...
}
@CookieValue
1
2
3
4
@GetMapping("/demo")
public void handle(@CookieValue("JSESSIONID") String cookie) {
//...
}
BindingResult
1
2
3
4
public interface BindingResult extends Errors {
Map<String, Object> getModel();
// ......
}
返回值
| 返回值类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @ResponseBody | 使用 HttpMessageConverter处理结果 |
| String | 一个view的名字,会被ViewResolver处理 |
| ModelAndView | The view and model attributes to use |
……
参数校验
使用 @Valid 标记需要校验的参数,可以使用 BindingResult 或 Errors 来获取校验异常。
注意参数的位置 BindingResult 要紧跟 @Valid 标注的参数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
@PostMapping(value = "/signup")
public String signup(@ModelAttribute("user") @Valid UserDto userDto, BindingResult result, Model model){
Map<String,String> errors = new HashMap<>();
if (result.hasErrors()) {
result.getFieldErrors().forEach(e ->{
errors.put(e.getField(),e.getDefaultMessage());
});
}
model.addAttribute("errors",errors);
model.addAttribute("user", userDto);
return "signup";
}
在需要校验的类中添加校验注解,注解有很多。
@Max@Min@Negative@NegativeOrZero@Positive@PositiveOrZero
@NotBlank@NotEmpty@NotNull@Null
@Pattern
@Past@Future@PastOrPresent@FutureOrPresent– 约束时间是过去还是未来
@DecimalMax@DecimalMin@Digits
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public class UserDto {
@Pattern(regexp = "^[a-zA-Z][0-9a-zA-Z_]{5,63}$",message = "用户名格式不正确")
@NotBlank(message = "用户名不能为空")
private String username;
@Size(min=6, max=127,message = "密码格式不正确")
@NotBlank(message = "密码不能为空")
private String password;
@Size(min=6, max=127,message = "密码格式不正确")
@NotBlank
private String confirmPass;
@Pattern(regexp = "^\\d{5,15}@qq\\.com$",message = "邮箱格式不正确,当前只能使用QQ邮箱")
@NotBlank(message = "邮箱不能为空")
private String email;
}
简易的异常处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
<form action="/user/signup" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" name="${_csrf.parameterName}" value="${_csrf.token}"/>
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" id="username" autofocus="autofocus" value="${(user.username)!""}"/> ${(errors.username)!}<br/>
Email:<input type="text" name="email" id="email" value="${(user.email)!""}"/> ${(errors.email)!}<br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="password" id="password" value="${(user.password)!""}"> ${(errors.password)!}<br/>
再次输入密码:<input type="password" name="confirmPass" id="confirmPass" value="${(user.confirmPass)!""}"> ${(errors.confirmPass)!}<br/>
<input type="submit" value="注册" />
</form>
值得注意的是,使用 @Valid 注解,在校验失败时会抛出 MethodArgumentNotValidException。
@Validated
@Valid 不能用于校验 RequestParam 和 path variables,这时我们可以使用 @Validated 来应用校验。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
@Validated
public class RegistrationController {
@GetMapping
public Map search(@Email @RequestParam("email") String email) {
return emailMessage(email);
}
}
注意 @Validated 抛出的是 ConstraintViolationException。
跳转
在View的名字前加上特殊前缀 redirect:
forward: 会调用 RequestDispatcher.forward()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
@RequestMapping(value = "/add", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String addBookmark(Principal principal,@ModelAttribute Bookmark bookmark){
User user = userRepository.findByUsername(principal.getName());
bookmark.setUserId(user.getId());
bookmarkRepository.save(bookmark);
return "redirect:/bookmark/all";
}
异常处理
该抛异常的地方直接抛出异常。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public User getUserByUserId(final String userId) {
User user = userMapper.selectByUserId(userId);
if (user == null) {
throw new UserNotFoundException();
} else {
return user;
}
}
}
注册一个 @ControllerAdvice 的 Spring Bean 来处理异常。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
@ControllerAdvice
@RestController
public class ExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = UserNotFoundException.class)
public RestResult unknownUserException(UserNotFoundException ex) {
return RestResult.NOT_FOUNT().message("用户不存在").build();
}
// 此处统一处理 @Valid 产生的异常
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public RestResult paramValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException ex){
Errors errors = ex.getBindingResult();
Map<String,String> returnErrors = new HashMap<>();
if(errors.hasFieldErrors()){
errors.getFieldErrors().forEach(e -> returnErrors.put(e.getField(),e.getDefaultMessage()));
return RestResult.ERROR_PARAMS().data(returnErrors).message("参数不正确").build();
}
return RestResult.ERROR_PARAMS().message("参数不正确").build();
}
}